Introduction
Thailand, located at the heart of mainland Southeast Asia, is a bustling nation that has experienced significant economic growth over the past few decades. As a result of this rapid industrialization, the country’s capital city of, Bangkok has become a hub for commerce and tourism, drawing in millions of visitors each year.
However, the downside to this rapid growth has been the massive congestion that now plagues the city, with traffic jams and pollution becoming increasingly problematic. In addition, as the country has ramped up industrial activities, there has been a serious depletion of natural resources such as forests, water sources, and wildlife habitats.
Despite these challenges, Thailand remains a vibrant and diverse land, filled with stunning natural beauty, rich cultural traditions, and a thriving business sector. The government and private sector agencies are working together to solve these issues while continuing to promote sustainable development and maintain the country’s unique identity.
Jump to Introduction, Geography, Climate, People & Society, Economy, Insight, Google Maps, Facts, and Did You Know about Thailand. Or visit the driving directions page for routing instructions.
Geography
Located in northeastern Thailand, one-third of the country’s land area comprises a low plateau primarily drained by tributaries of the Mekong River. Rolling hills, plateaus, and patches of fertile soil suitable for agriculture characterize this region.
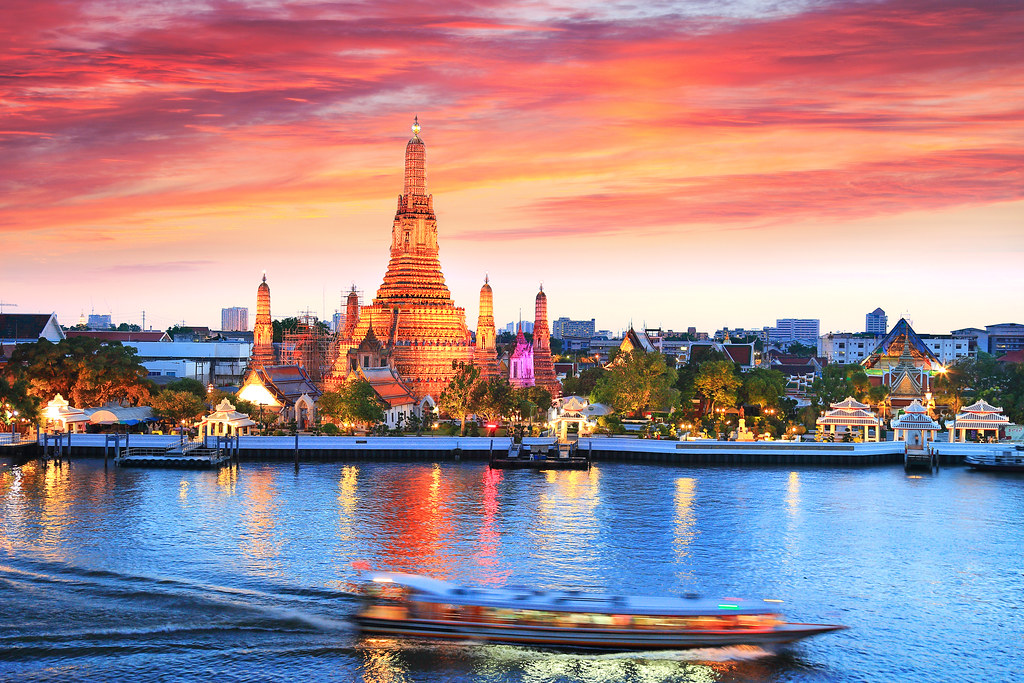

In contrast, the central plain is considered the most fertile area in the country. It stretches from north to south and is home to a vast network of rivers and canals that provide ample irrigation for rice and other crops. The central plain is where the Chao Phraya River, the country’s major river, flows into the Gulf of Thailand.
Due to its favorable geology, climate, and hydrology, the central plain has long been the agricultural heartland of Thailand. The region produces various crops, including rice, fruit, vegetables, and sugarcane, which are not only consumed domestically but also exported to other countries. Despite the central plain’s fertile soils and abundant natural resources, rapid urbanization and industrialization have pressured the region’s ecosystems and contributed to environmental and social challenges.
Climate
Thailand’s tropical climate is generally hot and humid throughout the year. The climate can be divided into three main seasons: hot, wet, and cool.
The hot season typically lasts from March to May and is characterized by high temperatures and humidity. During this time, temperatures can soar to 35°C or higher, making it one of the hottest times of the year. The heat is often exacerbated by occasional droughts, affecting agricultural production and water supply.
The wet season runs from May to October, with heavy rainfall from the southwest monsoon winds. This is when Thailand experiences most of its annual rainfall, with some parts of the country receiving more than 2,500 mm of rain annually. Floods are common during this time, particularly in low-lying areas and regions with poor drainage.
Finally, the cooler season runs from November to March, marked by cooler temperatures and lower humidity levels. Temperatures may drop to as low as 15°C in some parts of the country, particularly in the northern and northeastern regions. This season is considered the best time to visit Thailand, as the weather is relatively pleasant and there is less rainfall than during the wet season.
People & Society
Buddhism is considered a national binding force in Thailand, with over 90% of the population adhering to this religion. Buddhist culture and traditions are deeply ingrained in Thai society, influencing everything from daily rituals to major celebrations and festivals.
In Thailand’s northern and northeastern regions, approximately 600,000 hill tribes-people live in remote, mountainous areas. These groups have distinct cultures and languages, although many have been integrating into Thai society through education and other programs.
The Chinese minority in Thailand is the most assimilated in the region, having been present for several centuries. Many Thai-Chinese families have integrated into Thai society through intermarriage and cultural assimilation.
In the undeveloped far south of Thailand, Malay Islamists have been fighting for secession from the rest of the country for decades. The conflict has been marked by violence, with periodic bombings and attacks on civilians and security forces.
Thailand’s political history since the 2006 fall of populist Prime Minister Thaksin Shinawatra has been marked by instability, with frequent protests, multiple coups, and periods of military rule. The most recent coup occurred in 2014 when the military ousted the democratically-elected government. Political tensions continue to simmer in the country, although there have been some attempts to reconcile the disparate political factions and move toward greater stability.
The Economy
Thailand has a relatively thriving manufacturing sector, with electronics, textiles, and automobiles major employers and economic contributors. Additionally, Thailand is home to significant natural gas reserves, which are important for domestic energy needs and export.
Thailand is also a leading exporter of rice and rubber, with these products being major components of the country’s agricultural sector. However, political turmoil has sometimes impacted these industries, as protests and instability can lead to supply chain disruptions and decreased investor confidence.
Tourism is also a significant economic driver in Thailand, with the country being known for its beautiful beaches, vibrant culture, and delicious cuisine. However, the sex industry, in particular, has long been a controversial aspect of tourism in Thailand, harming the country’s image and leading to concerns about exploitation and human trafficking.
Thailand is unfortunately prone to natural disasters such as flooding, landslides, and tropical storms, which can cause significant damage to infrastructure, crops, and homes. These disasters can have far-reaching economic impacts, particularly in rural areas where agriculture is a key source of income.
Overall, while Thailand has many strengths as an emerging economy and popular tourist destination, it also faces significant challenges related to political stability, natural disasters, and the need to address social and environmental issues.
Insight
Thailand is the only country in Southeast Asia that was never colonized by a European power. The country’s full name, Prathet Thai, means “land of the free,” It has a long and proud history of independence.
While other countries in the region were subject to colonization by European powers, Thailand managed to maintain its independence through a combination of diplomacy, strategic alliances, and skillful navigation of international relations. Though Thailand suffered brief periods of foreign occupation by neighboring countries such as Burma and Cambodia, it was never subjected to the colonial rule that much of Southeast Asia experienced.
This independent streak has been an important part of Thailand’s national identity and is a point of pride for many Thais. While the country has not been without its political and social challenges over the years, its unique independence history has helped shape its culture and character.
Google Maps
Facts
Name: Thailand (Kingdom of Thailand), local name: Ratcha Anachak Thai
Languages: Thai (official language) only 90.7%, Thai and other languages 6.4%, only other languages 2.9% (includes Malay, Burmese)
ISO code: th, internet: .th
Capital city: Krung Thep (Bangkok), the city’s Thai name, means City of the Deity and is a shortening of the full ceremonial Krungthepmahanakhon Amonrattanakosin Mahintharayutthaya Mahadilokphop Noppharatratchathaniburirom Udomratchaniwetmahasathan Amonphimanawatansathit Sakkathattiyawitsanukamprasit; translated the meaning is: City of angels, the great city of immortals, magnificent city of the nine gems, the seat of the king, city of royal palaces, home of gods incarnate, erected by Vishvakarman at Indra’s behest; it holds the worlds record as the longest place name (169 letters), GPS: 13 45 N, 100 31 E
Time: UTC+7 (12 hours ahead of Washington, DC, during Standard Time) (No daylight saving time)
Population: 69,794,997 (2023 estimate) (Thai / Thai (also singular and plural))
Urban population: 52.2% (2021) – 10.723 million, Bangkok (capital city), 1.417 Chon Buri, 1.324 million, Samut Prakan, 1.182 million, Chiang Mai, 979,000 Songkla, 975,000 Nothaburi (2021)
Location: Southeastern Asia, bordering the Andaman Sea and the Gulf of Thailand, southeast of Burma. Thailand is a Southeastern Asian country. You may find 19 other countries on this continent.
Coordinates: 15 00 N, 100 00 E
Bordering countries: (4 nations): Burma 2416 km, Cambodia 817 km, Laos 1845 km, Malaysia 595 km
Land area: 510,890 sq km
Water area: 2,230 sq km
Total area: 513,120 sq km – About three times the size of Florida, slightly more than twice that of Wyoming.
Terrain: Central plain, Khorat plateau in the east, mountains elsewhere
Highest point: Doi Inthanon 2,565 m
Lowest point: Gulf of Thailand 0 m
Major rivers: Mekong (shared with Burma, Laos, China, Cambodia, and Vietnam) – 4,350 km, Salween (shared with China and Burma) – 3,060 km, Mun – 1,162 km
Natural hazards: Land subsidence in the Bangkok area resulting from the depletion of the water table; droughts.
National holiday(s): Birthday of King WACHIRALONGKON, 28 July (1952)
Did you know about Thailand?
- Thailand is the only country in Southeast Asia that was never colonized by a European power. As a result, Thai culture and traditions have remained largely intact.
- The world’s largest gold Buddha statue, the Golden Buddha, is located in Bangkok, Thailand. It is over 10 feet (3 meters) tall and weighs over 5 tons.
- Thai cuisine is known for its spicy flavors, and the country is home to some of the hottest peppers in the world. The “ghost pepper,” or bhut jolokia, is native to northeastern India and parts of Bangladesh but is widely used in Thai cooking.
- Thailand has over 1,400 islands and many popular tourist destinations. The most famous of these is Phuket, the largest island in Thailand, which attracts millions of visitors yearly.
- The Thai language has 44 consonants and 32 vowels, making it one of the most complex languages in the world to learn.
You may also be interested in Burma, Cambodia, Laos, and Malaysia.
Do you like this Thailand-related maps & fact page? Please don’t forget to share with others!